Meters & Sensors
Seeed Studio Grove Cape for BeagleBone Series
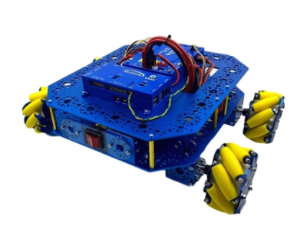
Seeed Studio Shield Bot
Compared with the previous version, The Shield Bot V1.1 can use the usb port of PC to charge battery. And the charging efficiency is greatly improved after we optimize the circuit. And you can use the Arduino/Seeeduino Vin pin to fast charge.
Note: Compatible Arduino Board not included, try the Seeeduino.
Seeed Studio Solar Charger Shield v2.2
Seeed Studio Xadow - UV Sensor
TinkerKit Hall Sensor module
TinkerKit Hall Sensor module creates a voltage related to the magnetic field around the sensor. This can be used to detect distance from a nearby magnet. Hall sensors can also be used to detect the magnetic field induced in a wire or coil.
TinkerKit Sensor Shield V.2
TinkerKit Sensor Shield V.2 allows you to hook up the TinkerKit Sensors and Actuators directly to the Arduino without the use of the breadboard. It has 12 standard TinkerKit 3 pin connectors.
TinkerKit Tilt Sensor module
TinkerKit Tilt Sensor module can detect when it is at an angle. This module contains two contacts and a small metal ball. When the sensor is in its upright position, the ball bridges the two contacts, completing the circuit. When the board is tilted, the ball moves, and the circuit opens. When upright, the module outputs 5V and when it is tilted, it outputs 0V. When connected to an input on the Arduino using the TinkerKit Shield, you can expect to read a value of 1023 when in its upright position and 0 when it is titled.
This module is sensor. The connector is an output, which must be connected to one of the input connectors on the TinkerKit Shield.
Vernier Goniometer
The Goniometer can be used to measure the dynamic motion of a limb during different types of physical activity.
- A set of elastic straps are used to secure the sensor to the subject.
- The lightweight and flexible joint arms allow the limb to move naturally.
- Use it with an EKG Sensor to measure muscle activity during limb motion.
- The sensor can also be detached from the base plate and flexible arms so it can be used in a variety of STEM and engineering activities.